Interest Rates Have Nowhere To Go But Up
Posted By thestatedtruth.com on April 11, 2010
From The New York Times
By NELSON D. SCHWARTZ
Published: April 10, 2010
Even as prospects for the American economy brighten, consumers are about to face a new financial burden: a sustained period of rising interest rates.Â
The shift is sure to come as a shock to consumers whose spending habits were shaped by a historic 30-year decline in the cost of borrowing.
“Americans have assumed the roller coaster goes one way,†said Bill Gross, whose investment firm, Pimco, has taken part in a broad sell-off of government debt, which has pushed up interest rates. “It’s been a great thrill as rates descended, but now we face an extended climb.â€
The impact of higher rates is likely to be felt first in the housing market, which has only recently begun to rebound from a deep slump. The rate for a 30-year fixed rate mortgage has risen half a point since December, hitting 5.31 last week, the highest level since last summer.
Along with the sell-off in bonds, the Federal Reserve has halted its emergency $1.25 trillion program to buy mortgage debt, placing even more upward pressure on rates.
“Mortgage rates are unlikely to go lower than they are now, and if they go higher, we’re likely to see a reversal of the gains in the housing market,†said Christopher J. Mayer, a professor of finance and economics at Columbia Business School. “It’s a really big risk.â€
Each increase of 1 percentage point in rates adds as much as 19 percent to the total cost of a home, according to Mr. Mayer.
The Mortgage Bankers Association expects the rise to continue, with the 30-year mortgage rate going to 5.5 percent by late summer and as high as 6 percent by the end of the year.
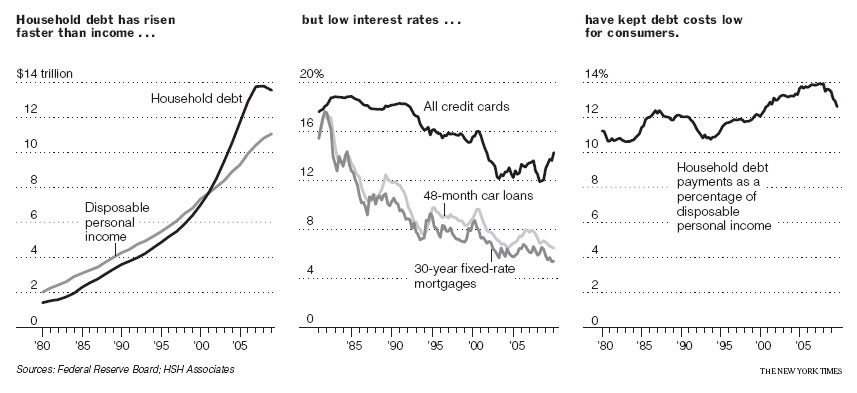
From that peak, steadily dropping interest rates have fed a three-decade lending boom, during which American consumers borrowed more and more but managed to hold down the portion of their income devoted to paying off loans.
Indeed, total household debt is now nine times what it was in 1981 — rising twice as fast as disposable income over the same period — yet the portion of disposable income that goes toward covering that debt has budged only slightly, increasing to 12.6 percent from 10.7 percent.
Household debt has been dropping for the last two years as recession-battered consumers cut back on borrowing, but at $13.5 trillion, it still exceeds disposable income by $2.5 trillion.

Comments